

- #Water cooled condenser design how to#
- #Water cooled condenser design manuals#
- #Water cooled condenser design install#
- #Water cooled condenser design full#

#Water cooled condenser design manuals#
#Water cooled condenser design install#
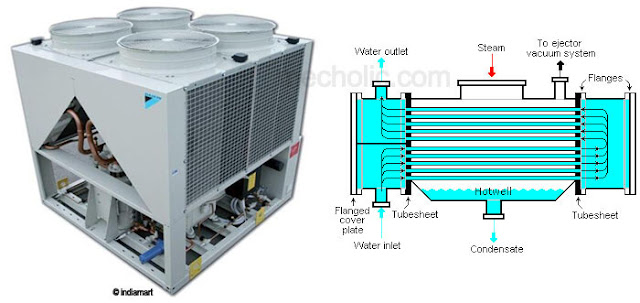
It is also generally easy to install and keep clean. No scale will develop on the tubes, either. You don’t have to worry about adding anything to it, and you don’t have to worry about the condensing medium freezing. The most obvious is that the units require no water to work. Chillers can also use devices called evaporators to remove heat, and then use the water-cooled condensers to take heat out of the evaporators, letting them go back to cooling the machines. Hot refrigerant vapor goes in sealed shells, where tubes or coils of cold water are. This type of condenser uses tubes of water to do the same job as the air in the air-cooled designs. Designs can come with horizontal or vertical discharge vents, and this will contribute to the shape of the chiller and where you can put them. You may see some small condensers using gravity to move the air.
The industrial machines will use fans to pull cool air from outside and eject hot air from the chiller.
#Water cooled condenser design full#
These tubes are full of hot gasses, which the air cools, causing the vapor to form a condensate on the tubing that drips into a reservoir or out a drain. There are a couple of types of condensers, classified by the type of medium used to cool the vapor. One common type in industrial applications is air cooled condensing units, also known by the acronym ACCU.Īir-cooled condensers push or pull air around a series of finned metal tubes. This pushes the refrigerant through the coils where the liquid will absorb heat from the chiller, causing it to become a vapor that will go through the process all over again. They generally sit around a compressor, which takes the now liquid refrigerant and pressurizes it.
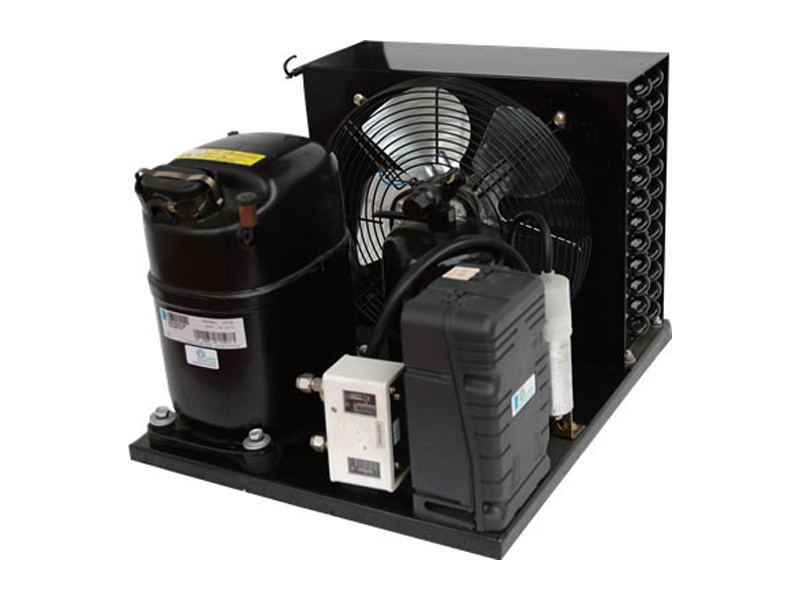

They get their name because they use a medium to absorb heat from a vapor of a refrigerant, which causes the vapor to condense to a (cooler) liquid. Basics Of Condensers In Chillersįrequently, chillers use units called condensers to cool the refrigerant (the chemical used to take heat from the cooling part of the machine.)Ĭondensers are a type of heat exchanger. A good place to start is a common type of cooling mechanism called a condenser. In order to decide on specifications for the chiller you need, you will have to develop a passing understanding of the features involved. They have a variety of features for cooling, and each mechanism has its own advantages. Picking the right chiller for your application means exploring many options.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
